
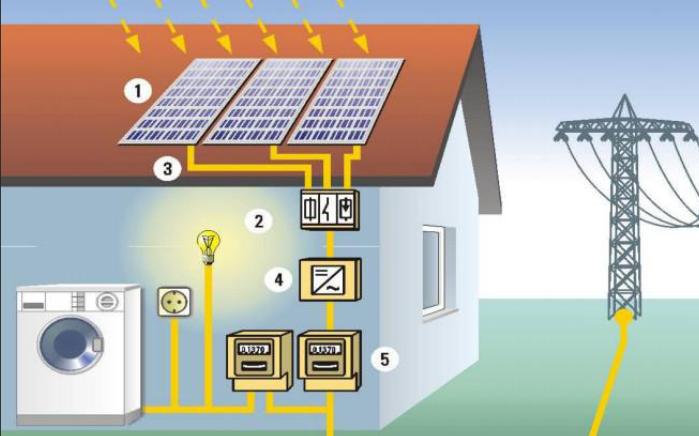
The main job of a home solar power system is to turn sunlight into electricity for your house and all your electrical devices. Let's take a closer look at how this happens.
First, there are the solar panels. You've probably seen them on many rooftops. They look like big, dark, flat rectangles. Most people install these panels on their roofs, but if you have a large, sunny yard, you can set them up there too.
Inside these solar panels are tiny parts called photovoltaic cells, and most of them are made from a material called silicon. Silicon has a very special property. When sunlight shines on it, it makes electrons (which are like super - tiny particles that carry electricity) start moving around. When these electrons move, they create an electric current, which is called direct current (DC). This is the first step in generating electricity from sunlight.
However, most of the appliances in our homes, like refrigerators, microwaves, and lights, use a different type of electricity called alternating current (AC). So, here comes the role of the inverter. The inverter is a very important part of the solar power system. Its main task is to convert the DC electricity generated by the solar panels into AC electricity that our homes can use.
But the inverter doesn't just change the current. It also constantly monitors how much power the solar panels are producing and controls the power output. This ensures that the system is working at its best all the time. Without a good inverter, the electricity from the solar panels wouldn't be suitable for powering our household appliances.
Once the electricity is converted into AC, it can be used immediately to power everything in your home. Lights will turn on, appliances will start working, and your home will have all the power it needs. But what if the solar panels produce more electricity than your home is using at a certain time?
Well, there are two main options. One is to store the extra power in a battery. Batteries are like big energy storage containers. You can use the stored energy later, such as at night when the sun isn't shining or on cloudy days. The other option is to send the extra electricity back to the electrical grid. In some places, the power company will actually pay you for this extra electricity you send back. This is called a feed - in tariff, and it's a great way to make some extra money from your solar power system.
As we mentioned before, PV panels are the most important part of a home solar power system. There are several types of PV panels available on the market, and each has its own characteristics.
Monocrystalline silicon panels are made from a single crystal of silicon. They are known for their high efficiency, often reaching up to 22% or more. This means they can generate a large amount of electricity from a relatively small area. They are a great choice for homes with limited roof space. However, they tend to be more expensive upfront. But in the long run, they can produce more power and save you more money on your electricity bills.
Polycrystalline silicon panels, on the other hand, are made from multiple silicon crystals. They are generally more affordable than monocrystalline panels. Their efficiency typically ranges from 15% to 20%. Although they are not as efficient as monocrystalline panels, they are still a very popular option, especially for those who are on a budget but still want to benefit from solar power.
Thin - film panels are made by depositing a thin layer of semiconductor material onto a substrate. These panels are the most lightweight and flexible among the three types. They can be easily installed on various surfaces, even curved ones. However, they generally have a lower efficiency, usually between 10% and 15%. Despite this, they are still a good choice in some specific situations, such as when the installation location has unique requirements for the weight and shape of the panels.
Inverters play a crucial role in the solar power system. There are two main types of inverters used in household PV systems: string inverters and microinverters.
String inverters are the most commonly used type. They are connected to multiple PV panels in a series, or “string.” They convert the combined DC output of the string into AC. String inverters are relatively cost - effective and are suitable for systems with a relatively uniform orientation and shading conditions. But if one panel in the string is shaded or underperforms, it can affect the performance of the entire string and reduce the overall power output.
Microinverters, on the other hand, are connected to each individual PV panel. This allows for independent monitoring and optimization of each panel's performance. Even if one panel is shaded or has a problem, the other panels can still operate at full capacity. Microinverters offer greater flexibility and can potentially increase the overall energy production of the system, especially in complex or shaded roof installations. However, they are generally more expensive than string inverters.
Mounting structures are used to securely install the PV panels on the roof or other surfaces. The choice of mounting structure depends on various factors, such as the type of roof (e.g., flat, pitched), the local climate conditions, and the aesthetic preferences of the homeowner.
For pitched roofs, roof - mounted racking systems are commonly used. These systems can be installed directly onto the roof tiles or shingles and provide a stable platform for the PV panels. They can be either flush - mounted, which gives a more streamlined look, or stand - off mounted, which allows for better ventilation and may be more suitable for areas with heavy snow or rain.
Flat roofs may require a different type of mounting structure. Ballasted systems use weights, such as concrete blocks, to hold the PV panels in place without penetrating the roof membrane. This is a good option for roofs that cannot support the weight of a traditional racking system or where roof penetration is not permitted. Penetrating roof - mount systems, on the other hand, involve drilling through the roof to install the mounting brackets. This method provides a more secure installation but may require additional waterproofing measures.
While not a necessary component for all household PV systems, batteries can significantly enhance the functionality and independence of the system. Batteries are used to store excess electricity generated by the PV panels during periods of high sunlight, such as during the day. This stored energy can then be used later, when the sun is not shining, such as at night or on cloudy days.
There are several types of batteries available for use in PV systems. Lead - acid batteries are the most commonly used and are relatively inexpensive. But they have a lower energy density, a shorter lifespan, and require more maintenance compared to other types of batteries. Lithium - ion batteries, on the other hand, offer a higher energy density, a longer lifespan, and faster charging times. They are more expensive upfront but are becoming increasingly popular due to their superior performance. Flow batteries are a newer type of battery that use liquid electrolytes to store energy. They offer the advantage of being able to store large amounts of energy and have a long lifespan, but they are currently more expensive and less common.
Home PV systems are a great, sustainable choice for homeowners. They allow us to generate our own electricity, reduce our energy costs, and do our part to protect the environment. As solar technology continues to improve and costs become more affordable, more and more people are expected to choose these systems. Whether you want to save money on your electricity bills, reduce your carbon footprint, or achieve greater energy independence, a household PV system could be the perfect solution for you. By harnessing the power of the sun, you can enjoy the benefits of a reliable and clean energy source for your home.
SEVEN.Ni
Subscribe to us to enjoy event prices and get some of the best prices.
 IPv6 network supported
IPv6 network supported

