
Power frequencies vary across countries, and understanding these differences is essential when traveling. Before your trip, check the power frequency used in your destination to ensure compatibility with your devices. This simple step will help you pack the right equipment, such as adapters or converters. Use this quick guide to navigate international power frequencies with ease.
Electric frequency describes the number of complete cycles of alternating current (AC) that occur in one second. We measure this in Hertz (Hz).
The idea of electric frequency started in the late 1800s. This was when someone invented the alternator, creating AC electricity. Alternating current enabled efficient power transmission over long distances and became the foundation of modern electrical grids.
Today, the most common electric frequencies worldwide are 50 Hz and 60 Hz. Countries around the world have adopted these standards for power transmission and distribution. They provide a steady and dependable electricity supply to homes, businesses, and industries. This supports the needs of modern technology and society.
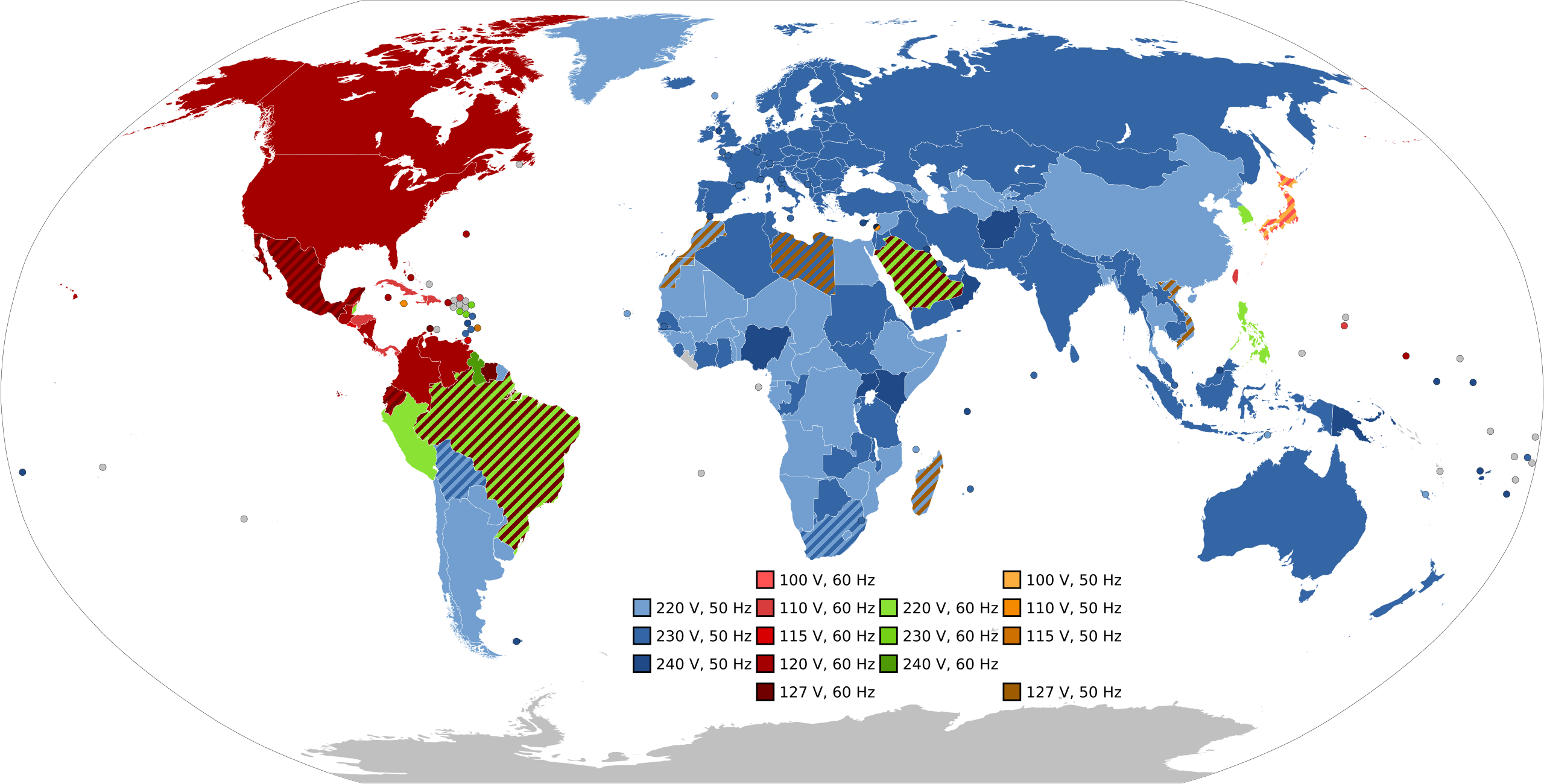
The widespread use of 50Hz frequency in these regions has its origins in the early days of electrical engineering. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, engineers in Europe and the UK set 50Hz as the standard for power transmission. This was during the rise of alternating current (AC) systems. Their decision influenced neighboring regions, setting a precedent for the adoption of 50Hz in many countries.
As other countries developed their electrical systems, they often turned to Europe for help. They adopted the 50Hz standard. Over time, this practice solidified 50Hz as the dominant frequency in Europe, most of Asia, Russia, Africa, and Australia.
Today, 50Hz gives millions of people a steady and reliable supply of electricity. This service helps shape the infrastructure and energy needs of modern society.
In contrast, the United States standardized its power grid on 60Hz. This choice, rooted in historical and technical considerations, became the defining characteristic of American electrical systems. Both 50Hz and 60Hz provide electricity. However, they have led to different developments in power grids worldwide.
At the start of the 20th century, the growth of alternating current (AC) systems led to a debate. People discussed what the best operating frequency should be. In the United States, Westinghouse Electric Corporation adopted 60Hz as the standard for their AC systems.
Meanwhile, General Electric Company in Europe chose 50Hz. This split created two incompatible systems. Over time, much of the world Europe's lead, adopting the 50Hz standard, while America remained steadfast with 60Hz.
The frequency difference affects the design and operation of electrical equipment. 60Hz systems are often better at sending power over long distances. They work well for high-power uses. Conversely, people often prefer 50Hz systems for local, lower-power distribution networks.
The choice between 50Hz and 60Hz depends on regional needs and infrastructure. Both frequencies have proven effective for over a century. Each suits particular applications, influenced by historical choices, equipment availability, and transmission requirements.
There is no absolute superiority of one over the other. The critical factor is frequency consistency. Stable and reliable frequencies ensure smooth operation of electrical equipment, while fluctuations can cause disruptions or inefficiencies. Both systems continue to support the global electrical grid, reflecting the adaptability of technology to meet diverse needs.
When traveling between regions with different power frequencies, equipment compatibility can become a challenge. If your device supports 50Hz but you find yourself in a 60Hz region—or vice versa—you'll need a frequency converter. This device ensures your equipment operates with the proper power supply while maintaining efficiency.
Using a frequency converter can protect your equipment from potential damage and improve its longevity. Before you travel, research trustworthy frequency converter manufacturers. This will help ensure smooth operation and peace of mind when using your equipment overseas.
YT Electric is the biggest OEM manufacturer of low-voltage AHF and SVG with more than 15 years' experience. All products hold certifications for ISO9001, CE, and CQC standards, and type test reports support them.
For information on how our 50/60Hz Active Harmonic Filter and Static Var Generator improve power quality: sales@ytelect.com
Keywords: 60 hz systems, north america, higher frequency, higher powered, 60 hz frequency, 60 hz power
hz power system, 20 higher speed, 50 hz power, frequency power, 400 hz, power line, frequency system, transmission lines
Subscribe to us to enjoy event prices and get some of the best prices.
 IPv6 network supported
IPv6 network supported

